Why male giraffes drink potential mates’ pee
In giraffes, an organ that detects pheromones has a stronger connection to the mouth than the nose. That’s different from many other mammals.
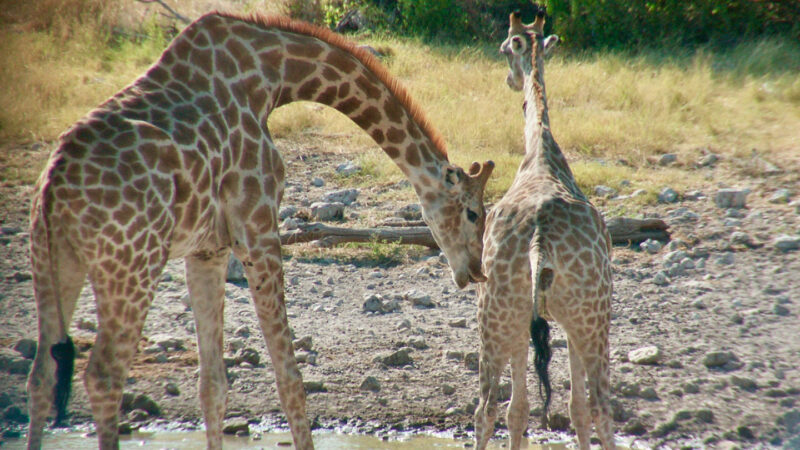

A female giraffe has a great Valentine’s Day gift for potential mates: urine.
Distinctive anatomy helps male giraffes get a taste for whether a female is ready to mate, animal behaviorists Lynette and Benjamin Hart report January 19 in Animals. A pheromone-detecting organ in giraffes has a stronger connection to the mouth than the nose, the researchers found. That’s why males scope out which females to mate with by sticking their tongues in a urine stream.
Animals such as male gazelles will lick fresh urine on the ground to track if females are ready to mate. But giraffes’ long necks and heavy heads make bending over to investigate urine on the ground an unstable and vulnerable position, says Lynette Hart, of the University of California, Davis.
The researchers observed giraffes (Giraffa giraffa angolensis) in Etosha National Park in Namibia in 1994, 2002 and 2004. Bull giraffes nudged or kicked the female to ask her to pee. If she was a willing participant, she urinated for a few seconds, while the male took a sip. Then the male curled his lip and inhaled with his mouth, a behavior called a flehmen response, to pull the female’s scent into two openings on the roof of the mouth. From the mouth, the scent travels to the vomeronasal organ, or VNO, which detects pheromones.
The Harts say they never saw a giraffe investigate urine on the ground.
Unlike many other mammals, giraffes have a stronger oral connection — via a duct — to the VNO, than a nasal one, examinations of preserved giraffe specimens showed. One possible explanation for the difference could be that a VNO-nose link helps animals that breed at specific times of the year detect seasonal plants, says Benjamin Hart, a veterinarian also at the University of California, Davis. But giraffes can mate any time of year, so the nasal connection may not matter as much.