Stool Capsules: Medicine from Human Waste? Revolutionary Therapy Offers Hope for Gut Diseases
In a groundbreaking development in medical science, researchers are now using human feces to develop medicines that treat severe intestinal disorders.
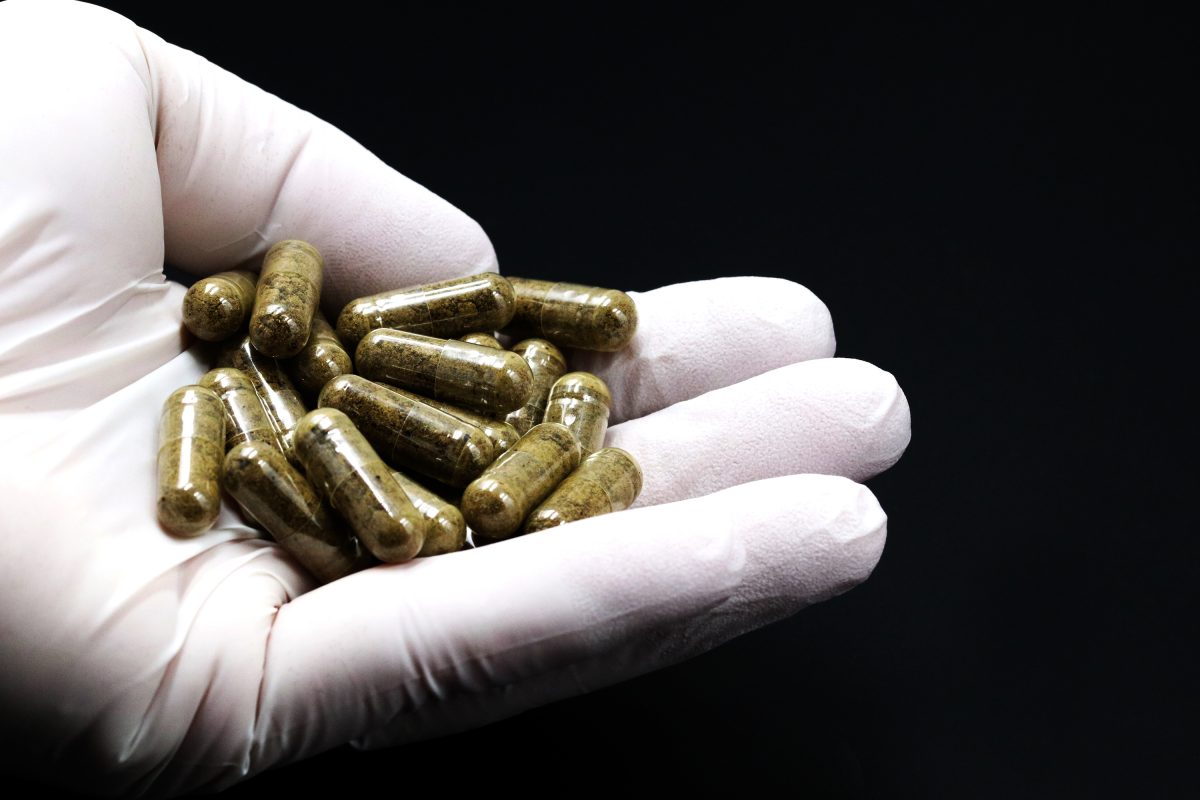

In a groundbreaking development in medical science, researchers are now using human feces to develop medicines that treat severe intestinal disorders. Known as Fecal Microbiota Transplantation (FMT), this therapy involves processing stool from healthy individuals to extract beneficial gut bacteria and encapsulating them into what are called “stool capsules.”
What Are Stool Capsules?
Stool capsules are oral medications that look like regular pills but contain microbiota from the human gut—a diverse community of beneficial bacteria crucial for digestion and immunity. These capsules are administered to patients whose natural gut flora has been disrupted, often due to heavy antibiotic use.
How Are They Made?
Stool from a screened, healthy donor is processed to remove harmful pathogens and isolate useful microbes. These are then dehydrated and placed into odorless, tasteless capsules for oral consumption.
Which Diseases Can It Treat?
The most successful use of stool capsules has been in treating Clostridioides difficile (C. diff) infection, a life-threatening intestinal disease often caused by overuse of antibiotics.
FMT therapy has shown a success rate of over 90% in such cases. Ongoing research is exploring its use in a variety of other conditions, including:
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) – such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) – relief from digestive symptoms
Autism Spectrum Disorder, Obesity, Diabetes, Parkinson’s Disease, and Liver Disorders – promising early-stage research
Is This Available in India?
Yes, but on a limited basis. Institutes like AIIMS Delhi, PGI Chandigarh, and CMC Vellore are conducting clinical trials and research on this therapy. It is not yet widely available and is used only in select, carefully monitored cases.
Safety and Regulations
All donors are rigorously screened for infections and other health issues.
The process follows strict hygiene and bio-safety protocols.
In countries like the U.S., it is FDA-regulated under investigational use, and in India, it comes under DCGI guidelines for limited clinical applications.
What was once considered medical waste is now proving to be a potential lifesaver. Stool capsules are opening a new frontier in microbiome-based therapies, offering hope where conventional treatments have failed.